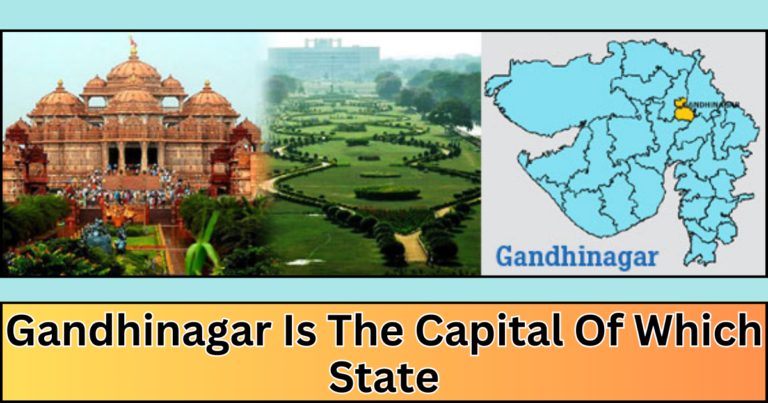
gandhinagar belongs to which state
gandhinagar belongs to which state : gandhinagar belongs to which state Gandhinagar, city, capital of Gujarat state, west-central India. It lies on the banks of the Sabarmati River, just north of Ahmadabad.Gandhinagar was named for Mohandas K. Gandhi, leader of the Indian nationalist movement. Built to supplant Ahmadabad as capital, the city was begun in 1966. State government offices were transferred to Gandhinagar in 1970, and the city subsequently became a commercial and cultural centre in Gujarat.
An expressway connects Gandhinagar with Ahmadabad. Pop. (2001) 195,985; (2011) 206,167.The capital of Gujarat, Gandhinagar (“city of Gandhi”) is named after Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, the native son of Gujarat revered worldwide as the Mahatma, the “Great Soul.” Gujarat, called the melting pot of India and treasure trove of architectural styles, derives its name from Gujjara-ratta, the form it takes in Prakrit, the ancient Indic dialect. Its Sanskrit name, Gurjjara-rastra, literally means the “country of the Gurjjaras.” The Gurjjaras were a Central Asian tribe, believed to have entered India along with the Huns in the mid-fifth century, when the imperial control of the Guptas was in decline.
The region the Gurjjaras settled was called Gujarat by the tenth century, when Mulraj Solanki, the founder of the Hindu Chalukyan dynasty, established his capital at Anhilwara Patan. Anhilwara in time came to be replaced by Ahmedabad, which was selected by Muzaffar Khan as his sultanate’s capital in 1412. In time, the city came to rival Manchester, U.K., in textiles. Bombay (present-day Mumbai) became the capital of the region when the British placed Gujarat under their Bombay presidency, and it was not until 1960, after the unilingual (Gujarati) state of Gujarat had been created from bilingual Bombay, that Gandhinagar, about 15 miles (24 km) north of Ahmedabad on the right bank of the Sabarmati River, was selected as the site of the capital city for the new state.
The selection of the site for the new capital was not without controversy. Princely Baroda (present-day Vadodara) and industrial Ahmedabad both wanted the honor of being named the capital city. But Baroda was ruled out because of its princely status, which was deemed incongruent with the democratic properties of independent India. Moreover, Fatesinghrao Gaekwad, the ruler of Baroda, was of Maharashtrian origins, which was not viewed favorably in Gandhi’s Gujarat. Ahmedabad was ruled out because of its overcrowded character, even though the mill owners, led by Ambalal Sarabhai and Kasturbhai Lalbhai, lobbied very hard to shift the capital to Ahmedabad.
Gandhinagar became a battleground for the competing ideals that had surfaced during the building of Chandigarh and Bhubaneswar. The mill owners of neighboring Ahmedabad, backed by Indian architect and planner Balakrishna Doshi, wanted the American architect Louis Kahn to build Gandhinagar as a worthy rival to Le Corbusier’s Chandigarh. There was, however, tremendous political pressure to make Gandhinagar a purely Indian enterprise, partly because the state of Gujarat was the birthplace of Mahatma Gandhi.
Even though, in the end, negotiations with Kahn broke down over payment in U.S. dollars, he exercised some influence in the construction of Gandhinagar from Ahmedabad, where he was building the Indian Institute of Management campus. The Gujarat government also considered the option of creating a consortium of private Indian architects, including Doshi, Charles Correa, Achyut Kanvinde, Hasmukh Patel, and others; but in the end the government recruited American-trained Hargobind K. Mewada, who had apprenticed with Le Corbusier in Chandigarh, to complete the project. The development of Gandhinagar, like its older cousins Chandigarh and Bhubaneswar, was in part an educational experiment and social welfare project, as well as a venture in professional city planning and architecture.
Historical Importance of Gujarat – Sites of Ancient Indus Valley Civilization
- Gujarat has 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley Civilisation.
- Gujarat has more sites of the Indus Valley Civilisation than any other state.
- Some of the most important sites of the Indus Valley Civilisation in Gujarat are Lothal, Dholavira, and Gola Dhoro.
- 5 rare seals were found in Gola Dhoro.
- Dholavira is the 5th largest site of this ancient civilisation.
- The world’s first dry dock was located in Lothal.
- During the rule of the Saka dynasty, the Gupta empire, and the Maurya empire, Khambhat and Bharuch served as ports and trading centres.
Gujarat – Economy
- The economy of Gujarat is the 4th largest in India.
- In the Human Development Index (HDI), Gujarat occupies the 21st position.
- Gujarat is a manufacturing hub in India.
- Gujarat is a highly industrialised state in India.
- In the sphere of the pharmaceutical industry, Gujarat is ranked in the 1st position. 28% of the drugs exported are from Gujarat, and 33% of the drugs manufactured in India are from the state of Gujarat.
- The ports of Gujarat handle 40% of India’s ocean cargo.
- Gujarat ranks second among Indian states in nuclear electricity generation.
- Gujarat ranks first in gas-based thermal electricity generation.
- In India, Gujarat has the lowest unemployment rate.
- 85% of Gujarat’s villages are connected through all-weather roads.
- Reliance operates the largest refinery in Gujarat.
Climate of Capital of Gujarat
- Gandhinagar’s climate has three distinct seasons: a hot and dry summer, a mild and pleasant winter, and a monsoon season with moderate rainfall.
- Summer temperatures often soar above 40°C (104°F), making it one of the hottest regions in India during this season.
- The city’s monsoon season typically occurs between June and September, relieving the scorching summer heat and replenishing the region’s agricultural lands.
- Like much of North India, Gandhinagar’s winter season typically spans from December to February.
- Daytime temperatures during the winter season in Gandhinagar typically range from 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F), making it comfortable for outdoor activities.
Demographics Capital of Gujarat
As per the 2011 Census, the demography of the capital of Gujarat is provided below:
| Demography Label | Value |
|---|---|
| Geo Location | 23.56 to 23.01 north latitude, east longitude 73.33 to 72.33 |
| Area Sq. Km | 2140 |
| Area (Rural) Sq. Km | 1763.41 |
| Area (Urban) Sq. Km. | 376.59 |
| Total Population (2023) | 8,772,000 |
| Total Male Population | 723,864 |
| Total Female Population | 667,889 |
| Average Literacy % | 84.16 |
| MCD | Gandhinagar Municipal Corporation |
| Municipalities | 4 (Pethapur, Mansa, Kalol and Dahegam municipality) |
Capital of Gujarat – Facts
- Architects H.K. Mewada and Prakash M. Apte planned and designed the city, making it the second planned city in the country after Chandigarh.
- It is divided into 30 sectors, each with its own shopping center, school, recreational areas, and residential areas.
- It is known as the ‘Tree Capital of India,’ with 54% of the land area covered with green forest.
- It is home to the administrative offices and Gujarat State Secretariat, also known as Sachivalaya.
- Gandhinagar became the host city for the Vibrant Gujarat Global Summit (G2 Summit), an event that brings together entrepreneurs, business leaders, and policymakers worldwide to promote economic growth in the country.
- The city is also home to Gujarat Aerospace and Defense Manufacturing Hub (GIDH), an industrial park dedicated to the aerospace and defense sectors.
In conclusion, Gandhinagar is a symbol of India’s commitment to Mahatma Gandhi’s principles and aspirations for sustainable urban development. As the capital of Gujarat, it plays a pivotal role in the state’s economy, culture, and administration. With its rich history, diverse demographics, and unique blend of tradition and modernity, Gandhinagar continues to grow and evolve, offering both challenges and opportunities that shape its future and contribute to the progress of Gujarat and India as a whole.
FAQ
What is the capital of Gujarat state?
Gandhinagar is the capital of the state of Gujarat in India. Gandhinagar is located approximately 23 km north of Ahmedabad, on the west central point of the industrial corridor between the metropolitan cities of Delhi and Mumbai.
Is Gandhinagar a part of Ahmedabad?
Ahmedabad and Gandhinagar are two separate cities in Gujarat. Gandhinagar is the capital, while Ahmedabad is the hub for commercial activities. Being adjacent, there is a blur sometimes about where Ahmedabad ends and Gandhinagar begins.
Why Gandhinagar is capital not Ahmedabad?
Because of the development of the territory of Gujarat, the capital of the state was kept at Ahmedabad. At that point, to diminish populace thickness of Ahmedabad city, Gandhinagar, the new capital of the territory of Gujarat, was set up. The city of Gandhinagar was set up on 2 August 1965.
What is the old name of Gandhinagar?
Phase 1: After the city’s infrastructure was completed in 1970, and until 1980, it was known as ‘Gandhian City,’ since it was based on Gandhi’s concepts and principles. Phase 2: Between 1980 and 1990, a time of low pollution, it was known as ‘Unpolluted City’.
When was capital shifted from Ahmedabad to Gandhinagar?
In 1970, the capital of Gujarat shifted from Ahemdabad to Gandhinagar.

I’m a professional content writer. I have experience of 5+ years in copywriting & content Writing.